Get to Know …
… and understand ICC Incoterms® 2020 !
Master the risks and costs of your international operations !

What Are Incoterms?
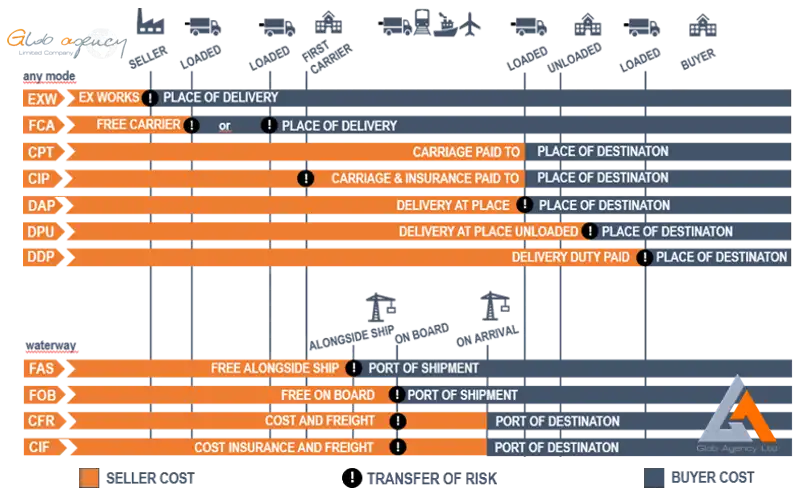
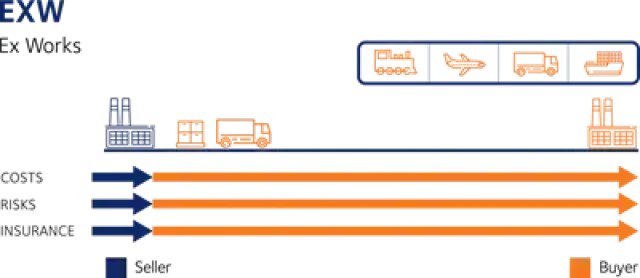
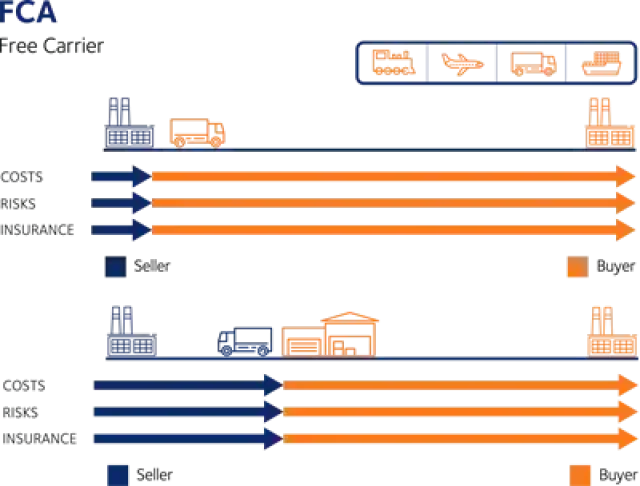
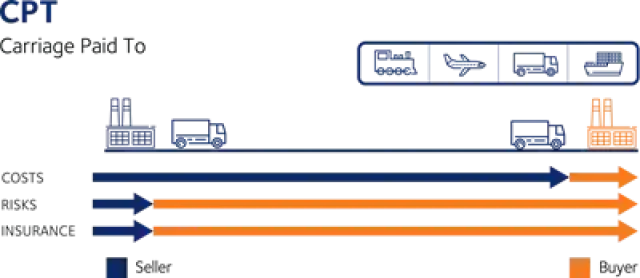
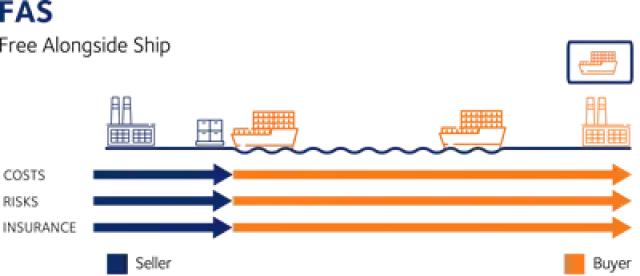
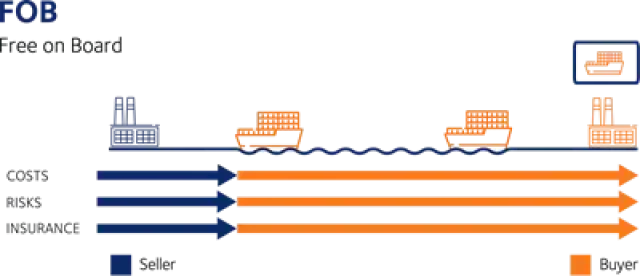
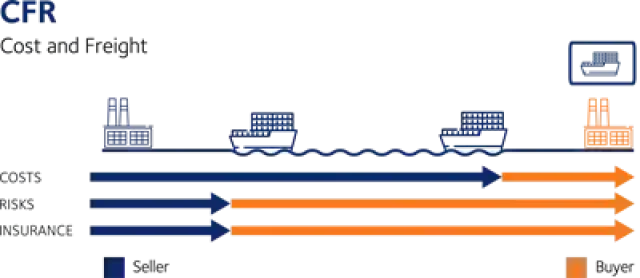
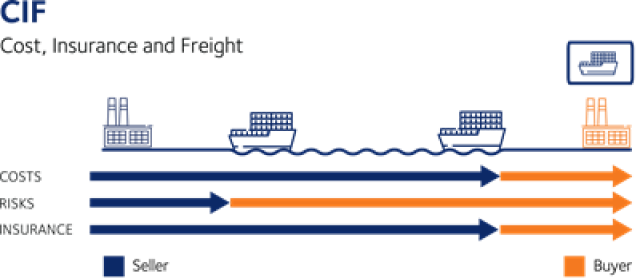
Incoterms are an internationally recognized set of terms that define the responsibilities and obligations of the parties involved in the transport of goods. Incoterms are used to clearly communicate the division of the cost of carriage and risks associated with the international transportation and delivery of goods between the seller to the buyer.
Incoterms were first introduced in 1936 by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) as different practices and legal interpretations between traders around the world necessitated a common set of rules and guidelines for interpreting the most commonly used terms in foreign trade. Incoterms are revised periodically, roughly every 10 years, by the ICC to conform to changing trade practices.
What Incoterms Do
It is important to note that the Incoterms of a contract for sale pertain only to the delivery terms (carriage freight costs) and insurability of the product. Incoterms define the respective obligations, costs and risks involved in the delivery of goods.
What Incoterms Do Not Do
Incoterms by themselves do NOT:
Specify the amount of the contract or the terms of financing,Supersede the law governing the contract, Address the transfer of ownership of the goods, Will not release funds for the delivered goods, Determine when revenue is recognized, Address the consequences of a breach of contract or exemptions of liability.
These items are defined by the terms of the sales contract and the governing law.